From industrial kitchens to contemporary homes, concrete countertop have come a long way in establishing their mark in the interior design industry. Known for their durability, aesthetics, and flexibility, concrete countertops are increasingly becoming the go-to choice for homeowners, contractors, and interior designers alike. As we discuss about these robust and versatile work surfaces, we encounter an essential element that plays a crucial role in their creation; concrete countertop forms.
Concrete countertop forms are integral tools used in shaping and molding the concrete into the desired countertop shape and size. Essentially, they act as the ‘mold’ or ‘skeleton’ onto which the concrete mixture is poured and left to cure. Once the concrete has hardened, the forms are removed, revealing a beautifully shaped concrete countertop.
This crucial component- the Concrete countertop form, allows for limitless creativity, enabling you to create countertops with a variety of edge details and shapes. You can choose from traditional, square edges, or opt for more intricate, rounded, or scalloped edges. The sky’s the limit when it comes to customization, and that’s primarily because of the flexibility these forms provide.
Understanding different types of concrete countertops forms, how to choose a concrete countertops form that suits your needs, and how to use concrete countertops forms effectively are crucial steps towards mastering the art of concrete countertop creation. This knowledge ensures a smooth process, saves valuable time and resources, and most importantly, helps achieve a flawless finished product.
So, whether you are a DIY enthusiast, a professional contractor, or simply someone interested in understanding more about this fascinating process, this comprehensive guide aims to offer valuable insights into the types, materials, and uses of concrete countertop forms.
1. What Are Concrete Countertop Forms?
As we explore the subject of concrete countertops, it’s essential to understand one of the critical components of their creation – the concrete countertop forms. But what exactly are they, and why are they such an important part of the process? Let’s break it down.
In the simplest of terms, concrete countertop forms are tools used to shape and mold concrete into desired countertop shapes and sizes. Imagine the form as the canvas on which a beautiful piece of art (in this case, your concrete countertop) will be created. It’s a supportive framework that guides the concrete mixture into a precise shape while it hardens.
Concrete countertop forms are typically made from various materials, such as rubber, foam, or even wood. The forms serve as a guide for the wet concrete, confining it to the desired shape until it hardens into a solid state. Once the concrete cures fully, the forms can be carefully removed to reveal a perfectly shaped concrete countertop.
The primary function of concrete countertop forms, therefore, is to provide a structured shape to the countertop during the casting process. But it’s not just about utility – forms are a canvas for creativity too. With the right forms, one can produce a myriad of different styles, including sleek, straight edges, elegant rounded corners, or even intricate decorative edge designs.
So why are forms such an integral part of the concrete countertop creation process? The answer lies in the unique properties of concrete. When freshly mixed, concrete is a semi-liquid material that can be poured and manipulated into various shapes. But as it hardens, it transforms into a solid, durable, stone-like surface. Without forms to guide and shape it during this transformation process, creating a precise and well-designed countertop would be near impossible.
By helping to mold and shape the concrete, forms play an indispensable role in achieving an aesthetically pleasing countertop with smooth, well-defined edges and consistent thickness. They allow for customization and uniqueness in the designs, enabling homeowners to get the exact look they desire for their kitchen or bathroom.
Choosing the right form and knowing how to use it effectively is equally important, and we’ll discuss this in the following sections. Concrete countertops forms are available in a variety of types, each suited for specific uses. The choice of form can significantly influence the finished product’s appearance and functionality.
2. Different Types of Concrete Countertop Forms
As the world of concrete countertops continues to evolve and expand, one element that remains crucial to this creative process is the concrete countertop form. Forms are the tools that shape, mold, and perfect the semi-liquid concrete mixture into a hard, stylish, and functional countertop. They are the cornerstone that allows homeowners, contractors, and DIY enthusiasts to let their imaginations fly, transforming their kitchens or bathrooms into uniquely styled spaces.
Choosing the right type of concrete countertop form can significantly impact the end product, both aesthetically and functionally. With various types available, each offering distinct advantages and disadvantages, it’s essential to know which form is best suited for your specific project. This comprehensive guide will delve into five popular types of concrete countertop forms, discussing their properties, pros, cons, and specific use-cases.
2.1 Pre-cast Forms : Type of Concrete Countertop Form
Pre-cast forms are molds used for creating concrete countertops off-site. The countertop is cast, cured, and finished before being transported to its final location.
Pros:
- Offers control over the curing conditions, enhancing the quality of the final product.
- Allows the inclusion of intricate details and unique embedded elements.
- Gives more room for experimentation with various finishing techniques.
Cons:
- Transportation of the cured countertop can be challenging and risky.
- Requires a separate, adequately large space for casting and curing.
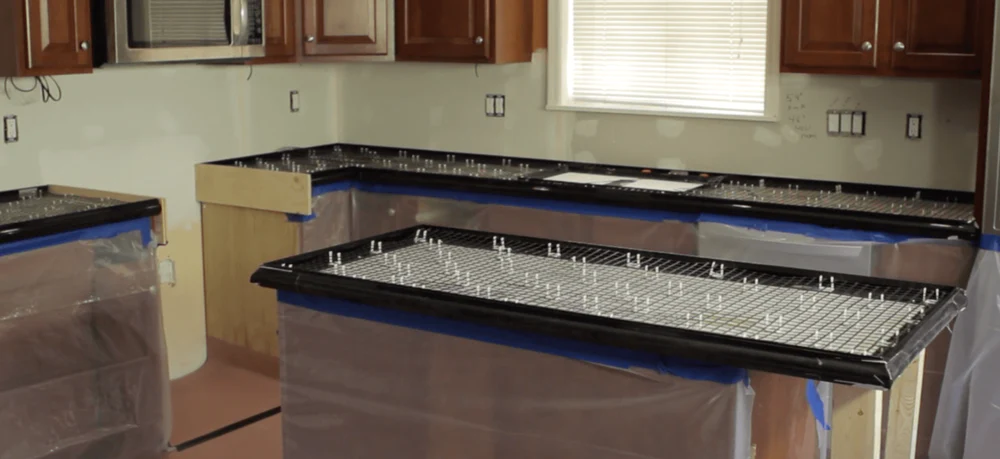

2.2 Pour-in-place Forms : Type of Concrete Countertop Form
Pour-in-place forms are used to create concrete countertops directly on top of the cabinets at the final location, eliminating the need for transportation.
Pros:
- Eliminates risks associated with transporting a heavy, pre-cast countertop.
- Ensures a perfect fit as the countertop is cast directly at the installation site.
- Ideal for large, complex, or uniquely shaped countertops.
Cons:
- The process can be messy, requiring protection for surrounding areas.
- Offers less control over the curing environment, which could potentially impact the countertop quality.

2.3 Foam Forms : Type of Concrete Countertop Form
Typically made from polystyrene foam, foam forms are lightweight, easy to shape, and commonly used for pour-in-place countertops.
Pros:
- Lightweight and easy to cut and shape, perfect for unique edge designs.
- Typically more affordable than other form types.
- Flexible, allowing easy removal after the concrete has cured.
Cons:
- Fragile and may not be suitable for larger, heavier countertop designs.
- Requires careful handling to prevent damage.

2.4 Rubber Forms : Type of Concrete Countertop Form
Made from flexible rubber, these forms can be bent and manipulated to create a multitude of unique shapes and edge designs.
Pros:
- Reusable, making them cost-effective for frequent use.
- Durable and resistant to tearing, capable of withstanding the rigors of concrete pouring.
- Easy to remove after curing, minimizing the risk of damage to the countertop.
Cons:
- Higher initial cost compared to other form types, although offset by longevity and reusability.
2.5 Fiberglass Forms : Type of Concrete Countertop Form
Fiberglass forms are sturdy, durable forms designed for repeat use, particularly suited for large-scale or commercial projects.
Pros:
- Provides a smooth, professional finish to the concrete countertop.
- Rigid and sturdy, excellent for large or heavy concrete designs.
- Long-lasting and reusable, making them cost-effective for frequent use.
Cons:
- Less flexible than rubber or foam forms, posing a challenge for complex or curvy designs.
2.6 Melamine Forms : Type of Concrete Countertop Forms
Melamine forms are made of melamine, a type of laminated plastic that’s known for its strength and smoothness. These forms are particularly used for pre-casting due to their ability to give a very smooth finish to concrete.
Pros:
- Provides a highly smooth finish due to its non-porous surface.
- Easy to cut and assemble, making them suitable for DIY enthusiasts.
- Relatively inexpensive and readily available.
Cons:
- Non-reusable, as the forms usually have to be broken to remove the cured countertop.
- Prone to chipping and scratching, which could potentially affect the finish of the countertop.
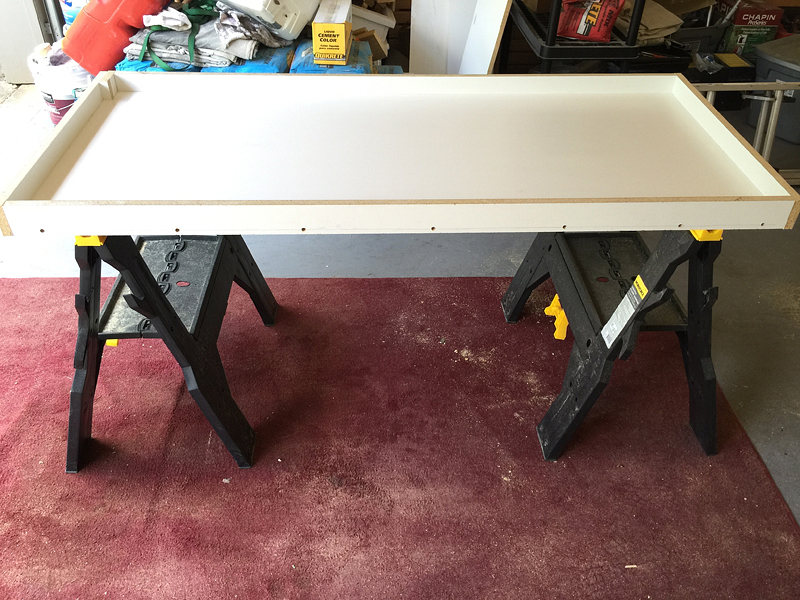

2.7 Acrylic Forms : Type of Concrete Countertop Form
Acrylic forms are made from a clear, thermoplastic material that offers excellent strength and durability. The transparency of these forms allows you to view the concrete as it’s poured and cured.
Pros:
- Transparent material allows monitoring of the curing process.
- Highly durable and reusable, offering long-term cost benefits.
- Resistant to damage from the environment and chemicals, ensuring longevity.
Cons:
- More expensive initially than other types of forms.
- Requires specialized tools to cut and shape, which may not be readily available to DIY enthusiasts.
2.8 Steel Forms : Type of Concrete Countertop Form
Steel forms are made from steel and are known for their extreme strength and durability. They’re typically used in commercial or industrial settings where they need to withstand heavy loads and repeated use.
Pros:
- Extremely durable and can withstand heavy loads.
- Can be used repeatedly, making them cost-effective for commercial use.
- Offers a sleek, modern finish to the concrete countertop.
Cons:
- Heavy and hard to work with, making them unsuitable for DIY projects.
- Can rust if not properly maintained, which could affect the countertop’s finish.
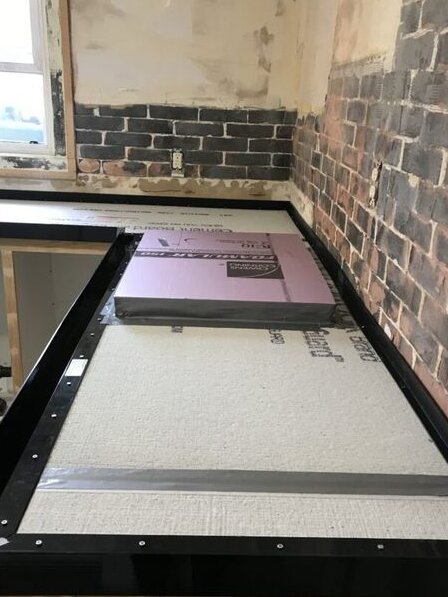

2.9 ABS Plastic Forms : Type of Concrete Countertop Form
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) plastic forms are robust and resistant to impact, chemicals, and heat. They are easy to work with and can be used for both pre-casting and pour-in-place methods.
Pros:
- Resistant to impact, chemicals, and heat, making them durable.
- Lightweight and easy to work with, suitable for DIY projects.
- Can be reused, offering cost-effectiveness over time.
Cons:
- Can be more expensive initially than other plastic or foam forms.
- May not offer as smooth a finish as melamine or acrylic forms.
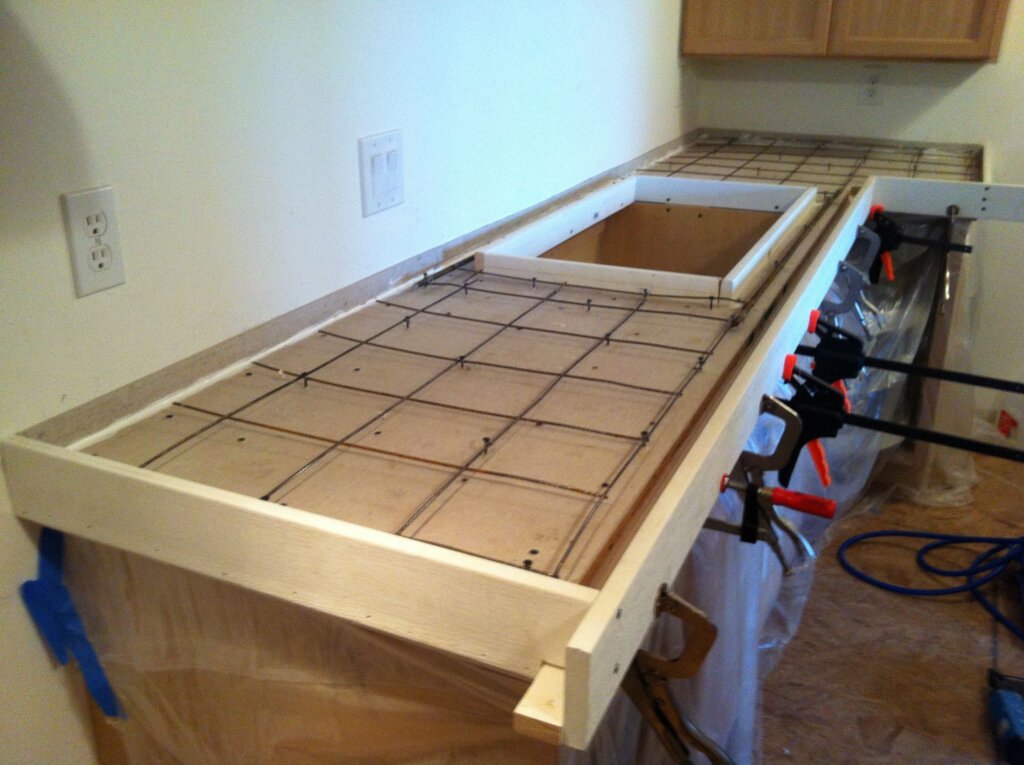
2.10 Wood Forms : Type of Concrete Countertop Form
Wood forms are traditional formwork materials and are typically used for creating rustic or natural-looking concrete countertops.
Pros:
- Adds a natural, rustic aesthetic to the countertop edge.
- Relatively inexpensive and readily available.
- Easy to work with, particularly for DIY enthusiasts.
Cons:
- Wood can absorb moisture from the concrete, which can lead to warping or distortion.
- Not as durable as other forms and may not be suitable for heavy or large countertops.

When choosing your concrete countertop forms, consider your project’s nature, the countertop design, your comfort level with the material, and the specific advantages and drawbacks of each form type. Knowledge of the types of concrete countertops forms, how to choose concrete countertops forms, and how to use concrete countertops forms can help ensure your project’s success, resulting in a beautiful and functional concrete countertop.
3. Materials Used in Concrete Countertops Form
Concrete countertop forms come in various materials, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks. Understanding the properties of these materials can guide you to the most appropriate choice for your project. In this section, we’ll explore some common materials used in the manufacture of concrete countertop forms:
3.1 Plastic
Plastic forms, including those made from acrylic or ABS, are lightweight, durable, and come in various shapes and sizes.
Benefits:
- Lightweight, which makes them easy to work with and maneuver.
- Generally cheaper than other materials, making them a budget-friendly option.
- Versatile and can be used for both pre-cast and pour-in-place methods.
Drawbacks:
- Not as durable as other materials like steel or rubber.
- Some plastic forms may not provide as smooth a finish as other materials.
3.2 Polystyrene
Polystyrene, a type of foam, is often used in pour-in-place forms because of its lightweight and easy-to-shape properties.
Benefits:
- Lightweight and easy to handle.
- Can be cut and shaped into a variety of unique designs.
- Affordable and easily available.
Drawbacks:
- Not as durable as other materials and may break or dent easily.
- Can be challenging to achieve a smooth, professional finish.
3.3 Rubber
Rubber forms are known for their flexibility, durability, and ability to create a multitude of shapes and designs.
Benefits:
- Extremely flexible, making them perfect for complex or unique edge designs.
- Resistant to wear and tear, providing longevity.
- Easy to remove after the concrete has cured, reducing the risk of damaging the countertop.
Drawbacks:
- More expensive than plastic or foam forms.
- Heavy and can be harder to work with compared to other materials.
3.4 Steel
Steel forms are robust and durable, often used in commercial and industrial settings.
Benefits:
- Highly durable and able to withstand heavy loads.
- Can be reused repeatedly, offering cost efficiency over time.
- Delivers a sleek, professional finish to the concrete countertop.
Drawbacks:
- Heavy and difficult to work with, making it unsuitable for DIY projects.
- Can rust if not properly maintained, potentially affecting the countertop’s finish.
3.5 Fiberglass
Fiberglass forms are lightweight, sturdy, and reusable, suitable for large-scale projects or commercial use.
Benefits:
- Lightweight yet strong, providing a balance between usability and durability.
- Reusable, offering cost benefits over time.
- Provides a smooth, professional-grade finish.
Drawbacks:
- Less flexible than rubber forms, posing a challenge for complex designs.
- Higher initial cost compared to other form materials.
3.6 Melamine
Melamine forms, made from a laminated plastic, are popular for their ability to provide a very smooth finish.
Benefits:
- Non-porous surface delivers a highly smooth finish.
- Easy to cut and assemble, making it a suitable choice for DIY projects.
- Relatively inexpensive and widely available.
Drawbacks:
- Forms usually need to be broken to remove the countertop, so they’re not reusable.
- Prone to chipping or scratching, which could affect the finished countertop’s surface.
3.7 Wood
Wood forms provide a natural, rustic look and are typically used for creating an earthy aesthetic.
Benefits:
- Adds a natural, unique aesthetic to the countertop edge.
- Easy to work with, particularly for DIY enthusiasts.
- Relatively inexpensive and readily available.
Drawbacks:
- Wood can absorb moisture from the concrete, leading to warping or distortion.
- Not as durable or reusable as other materials.
FAQ’s
How do I choose the right type of concrete countertop form for my project?
The right type of concrete countertop form for your project will depend on your budget, the complexity of the design you want, and the durability you need. If you are on a budget, molded plywood forms are a good option. If you want a more durable form, polyurethane or fiberglass forms are a good choice. If you want a custom shape, a custom form is the best option.
How do I prepare a concrete countertop form for use?
Once you have chosen a form, you will need to prepare it for use. This may involve sanding the form, applying a release agent, or both. You will then need to mix the concrete and pour it into the form. The concrete will need to cure for several days before it is ready to be used.
How do I pour concrete into a countertop form?
When pouring concrete into a countertop form, it is important to do so slowly and carefully. The concrete should be poured in a smooth, even layer. If the concrete is poured too quickly, it may not have time to set properly.
How long does it take for concrete to cure in a countertop form?
The curing time for concrete in a countertop form will vary depending on the type of concrete and the ambient temperature. However, it typically takes several days for the concrete to cure completely.
How do I use Concrete Countertop Forms?
Concrete countertop forms are used during the casting process. After choosing the right form, you place it on your base or casting surface, secure it, and then pour the concrete mixture into it. Once the concrete hardens, you remove the form to reveal the finished countertop.
What material is best for Concrete Countertop Forms?
The best material for concrete countertop forms depends on your specific needs. For instance, foam and plastic forms are lightweight and affordable, making them suitable for DIY projects. In contrast, steel and fiberglass forms are durable and reusable, making them ideal for commercial applications.
Can I reuse Concrete Countertop Forms?
The reusability of concrete countertop forms depends on the material. Steel, fiberglass, and some plastic forms can be reused, while foam, melamine, and some wood forms are typically single-use.
How do I achieve a smooth finish with Concrete Countertop Forms?
To achieve a smooth finish with concrete countertop forms, use forms made from materials like melamine, acrylic, or fiberglass, which provide a smooth surface. Also, ensure to vibrate the form after pouring the concrete to remove any air bubbles that might cause imperfections.
Are there any alternatives to traditional Concrete Countertop Forms?
Yes, in some cases, you can create your own forms using materials like melamine-coated particleboard or even sculpt the countertop edge by hand. However, these methods require skill and may not produce as professional a result as using commercial forms.
What are the costs associated with using Concrete Countertop Forms?
The cost of using concrete countertop forms varies widely, depending on the material and the form’s size and complexity. Foam and plastic forms are generally the most affordable, while steel and fiberglass forms are more expensive but can be reused, offering cost benefits over time.
How do I maintain my Concrete Countertop Forms?
Maintenance of concrete countertop forms involves cleaning them thoroughly after each use and storing them properly to prevent damage. For forms made of materials like steel, it’s essential to prevent rust by keeping them dry and applying a rust-inhibitor if necessary.


2 thoughts on “10 Concrete Countertop Forms : Types & Uses”