The American Concrete Institute (ACI) is an authority that has established guidelines and standards for concrete design and construction worldwide. It offers a comprehensive manual of concrete practice, known as the ACI Code, which incorporates valuable resources for concrete professionals. Among the key specifications and recommendations outlined in the ACI Code is the concept of minimum cover requirements for reinforcement. To ensure optimal performance and longevity in concrete structures, understanding and adhering to these requirements is of paramount importance.

1. Minimum Cover Requirements
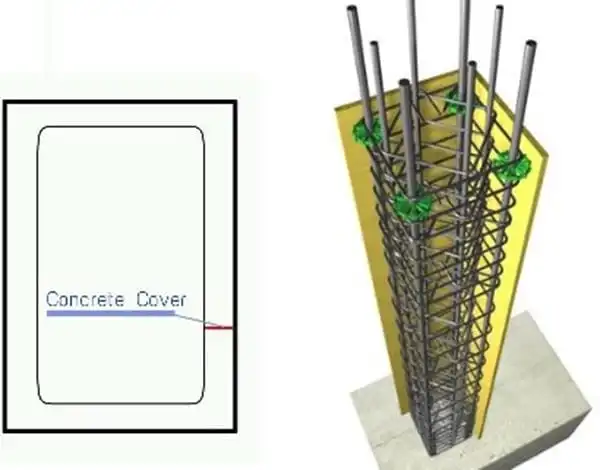
Concrete cover, often referred to as concrete cover, is the distance between the surface of the reinforced concrete and the nearest surface of the reinforcing bar (rebar). This cover is crucial to the structural integrity, durability, and safety of a concrete structure. The ACI Code provides explicit guidelines for minimum cover requirements.
These requirements dictate the minimum thickness of the layer of concrete that should surround the reinforcement, whether the reinforcement is positioned in a slab, wall, footing, or column. This minimum concrete cover serves several fundamental purposes that we will delve into in the following sections.
1.1 Ensuring Structural Durability and Longevity
The primary purpose of the concrete cover is to shield the embedded steel bars from potential environmental harm. A concrete structure is often exposed to various detrimental influences such as carbonation, chloride penetration, and other corrosive elements that could cause rusting and weakening of the steel reinforcement.
Adequate concrete cover thickness is crucial to delay the onset of corrosion in the reinforcement. As rust occupies a greater volume than steel, the resulting expansion creates tensile stresses in the concrete, leading to cracking, spalling, and eventual structural failure. Hence, the minimum cover requirements serve as a protective shield for the reinforcement against external threats, thereby enhancing the durability and lifespan of the structure.
1.2 Providing Fire Resistance
Fire resistance is a critical safety aspect of concrete structures. In a fire, concrete cover acts as a thermal barrier, protecting the reinforcement from the damaging effects of extreme temperatures. The greater the cover, the longer it will take for the heat to reach the reinforcing bars, thus increasing the fire rating of the structure.
In line with ACI standards, maintaining minimum cover requirements can prevent premature failure during a fire, safeguarding lives and properties. As such, these guidelines are not merely recommendations but a vital component of structural safety.

1.3 Ensuring Proper Bonding and Anchorage
Reinforced Concrete cover requirements also play an integral role in the bonding between reinforcement and concrete. An adequate cover ensures that the reinforcing bars are appropriately enclosed within the concrete, facilitating effective load transfer from concrete to the reinforcement and vice versa. This bond strength is crucial for the structure’s mechanical behavior, particularly under conditions of loading and deformation.
Moreover, the concrete cover contributes to anchorage – a key factor in the development length of the reinforcement. The development length is the necessary embedment length of the rebar within the concrete to enable the bar to reach its full strength capacity. As such, the concrete cover helps meet the anchorage requirements of the rebar, ensuring the structural integrity of the construction.
1.4 Meeting Aesthetic Requirements
From an aesthetic perspective, maintaining the ACI-specified minimum cover requirements prevents the reinforcing steel from becoming visible on the concrete surface (a phenomenon known as ghosting or shadowing). This is particularly important in architectural concrete applications where the visual appearance of the finished concrete structure is a primary concern.
1.5 Complying with Legal and Standardization Requirements
Lastly, adherence to the ACI’s minimum cover requirements is also a matter of legal compliance and standardization. The guidelines provided by the ACI are widely recognized and adopted in the American construction industry and are often enforced through local building codes and regulations. Non-compliance could lead to legal repercussions, rejected inspections, and a negative impact on the reputation of the involved parties.
Moreover, standardization enables easier communication and understanding between different parties involved in a construction project – from engineers and architects to contractors and inspectors.
2. Imperative of Following ACI’s Minimum Cover Requirements
Minimum cover requirements specified by the ACI Code serve multifaceted roles, each contributing to the structural integrity, durability, fire resistance, and aesthetic quality of a reinforced concrete structure. These guidelines also facilitate compliance with legal and industry standardization requirements. Adhering to these specifications is not only good practice but essential to the successful design and construction of concrete structures. By understanding the importance of these requirements, we can ensure that our structures meet the highest standards of safety, durability, and performance.
3. Minimum Cover Values for Different Structural Component as per ACI Code
ACI 318 is a standard for the design and construction of concrete structures. This standard also provides the guidelines for minimum concrete cover requirements for different structural components to ensure their durability and structural integrity. The standard specifies minimum concrete cover requirements for different conditions and elements, which are as follows:
- Concrete cast against and permanently exposed to earth: 75 mm (3 inches)
- Concrete exposed to earth or weather:
- No. 6 through No.18 bars: 50 mm (2 inches)
- No. 5 bar, W31 or D31 wire, and smaller: 40 mm (1.5 inches)
- Concrete not exposed to earth or weather:
- Slabs, walls, and joists: No. 14 and No.18 bars: 40 mm (1.5 inches); No. 11 bar and smaller: 20 mm (0.75 inches)
- Beams and columns: No. 14 and No.18 bars: 40 mm (1.5 inches); No. 11 bar and smaller: 40 mm (1.5 inches)
- Shells, folded plate members, and thin slabs: No. 6 through No. 10 bars: 20 mm (0.75 inches); No. 5 bar, W31 or D31 wire, and smaller: 15 mm (0.6 inches)
- Structural elements subjected to high corrosive environments (defined in the code) have higher minimum concrete cover requirements. The specific values should be referred to in the code.
All the bar sizes are mentioned in the US convention (i.e., No. X bar).
FAQ’s
What is the ACI Code’s minimum cover requirement for reinforcement?
The ACI Code’s minimum cover requirement for reinforcement varies depending on the concrete’s exposure condition and the size of the rebar. For instance, for concrete cast against and permanently exposed to earth, the cover should be 3 inches. However, for severe or very severe exposure conditions, a 2-inch cover is required for No. 6 through No. 18 bars.
Why is concrete cover important in reinforced concrete structures?
Concrete cover is crucial in reinforced concrete structures as it serves as a protective layer for the embedded steel bars. It shields the reinforcement from environmental harm, such as corrosion, ensures proper bonding and anchorage, provides fire resistance, meets aesthetic standards, and complies with legal and standardization requirements.
How does minimum cover requirement enhance the durability of concrete structures?
The minimum cover requirement enhances the durability of concrete structures by shielding the reinforcement from potential corrosive elements. This protective layer delays the onset of corrosion, thus preventing structural failure due to rusting and weakening of the steel reinforcement.
How does the concrete cover contribute to fire resistance?
The concrete cover acts as a thermal barrier in a fire, protecting the reinforcement from extreme temperatures. The greater the cover, the longer it takes for the heat to reach the reinforcing bars, thus increasing the fire rating of the structure.
Why is proper bonding between reinforcement and concrete important?
Proper bonding between reinforcement and concrete is vital as it ensures effective load transfer from the concrete to the reinforcement and vice versa. This bond strength is critical for the structure’s mechanical behavior, particularly under loading and deformation conditions.
What is the role of concrete cover in anchorage?
The concrete cover plays a crucial role in anchorage – a key factor in the development length of the reinforcement. The development length is the necessary embedment length of rebar within the concrete to enable the bar to achieve its full strength capacity.
What is ghosting or shadowing in concrete structures?
Ghosting or shadowing is a phenomenon where the reinforcing steel becomes visible on the concrete surface. Maintaining the ACI-specified minimum cover requirements prevents this from happening, ensuring the aesthetic quality of the finished concrete structure.
Is it mandatory to adhere to the ACI’s minimum cover requirements?
Yes, adherence to the ACI’s minimum cover requirements is a matter of legal compliance and standardization. The guidelines are widely recognized and enforced through local building codes and regulations. Non-compliance could lead to legal repercussions and rejected inspections.
What are the benefits of standardizing minimum cover requirements?
Standardizing minimum cover requirements facilitates easier communication and understanding between different parties involved in a construction project – from engineers and architects to contractors and inspectors. It ensures that structures meet the highest standards of safety, durability, and performance.
How does the ACI Code contribute to the successful design and construction of concrete structures?
The ACI Code, through its guidelines such as the minimum cover requirements, plays an integral role in the successful design and construction of concrete structures. These guidelines ensure that the structures meet the highest standards of safety, durability, fire resistance, and aesthetic quality.
Read More