The importance of recycling as a pillar of sustainable living and environmental conservation is evident worldwide. In the forefront of this crucial mission is California, a state known for its golden shores and progressive spirit. However, it faces a persistent challenge: enhancing the California’s recycling rate.
Despite its expansive economy and forward-thinking environmental initiatives, California’s actual recycling rate falls short of the ideal. As per CalRecycle, the department responsible for waste management and recycling in the state, California has not yet achieved its ambitious 75% recycling rate target for 2020. This reality begs an important question that our article explores: what recycling strategies can California implement to improve its recycling rate?
Tackling this question necessitates multifaceted recycling strategies. These strategies encompass a variety of sectors, including public education, waste management infrastructure, policy changes, and the promotion of a circular economy. These strategies aim not merely to enhance the California’s recycling rate, but to foster a culture of sustainable living and consistent recycling, thereby encouraging lasting and substantial change.
In this article, we delve into each of these recycling strategies, examining their current implementation, potential for improvement, and possible impact on improving California’s recycling rate. Our goal is not only to understand the present situation but also to inspire change and progress towards a more sustainable California.
Recycling isn’t solely the responsibility of government initiatives or corporate duties; it’s a collective effort that requires the involvement of every Californian. As this article explores strategies for improving California’s recycling rate, it offers an opportunity for readers to reflect on their role in this collective endeavor.
Understanding and applying successful recycling programs and adhering to California recycling laws are key components of these “recycling strategies. Enhancing the California’s recycling rate doesn’t merely rely on state-level action but also on the individual actions of every resident, from correct sorting and disposal to reducing consumption and reusing materials wherever possible.
Therefore, this journey towards improved recycling in California is shared. By implementing successful recycling strategies and obeying California recycling laws, we can make significant strides in improving the California’s recycling rate. This, in turn, will pave the way for a greener and more sustainable future for the Golden State.
1. Current State of Recycling in California
As the most populous state in the United States, California’s approach to waste management and recycling is of significant interest and importance. To truly comprehend the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead for recycling in the Golden State, it is essential to delve into the current state of affairs. An understanding of “recycling statistics California” and “current recycling rates” serves as the foundation for any meaningful discourse on the topic.
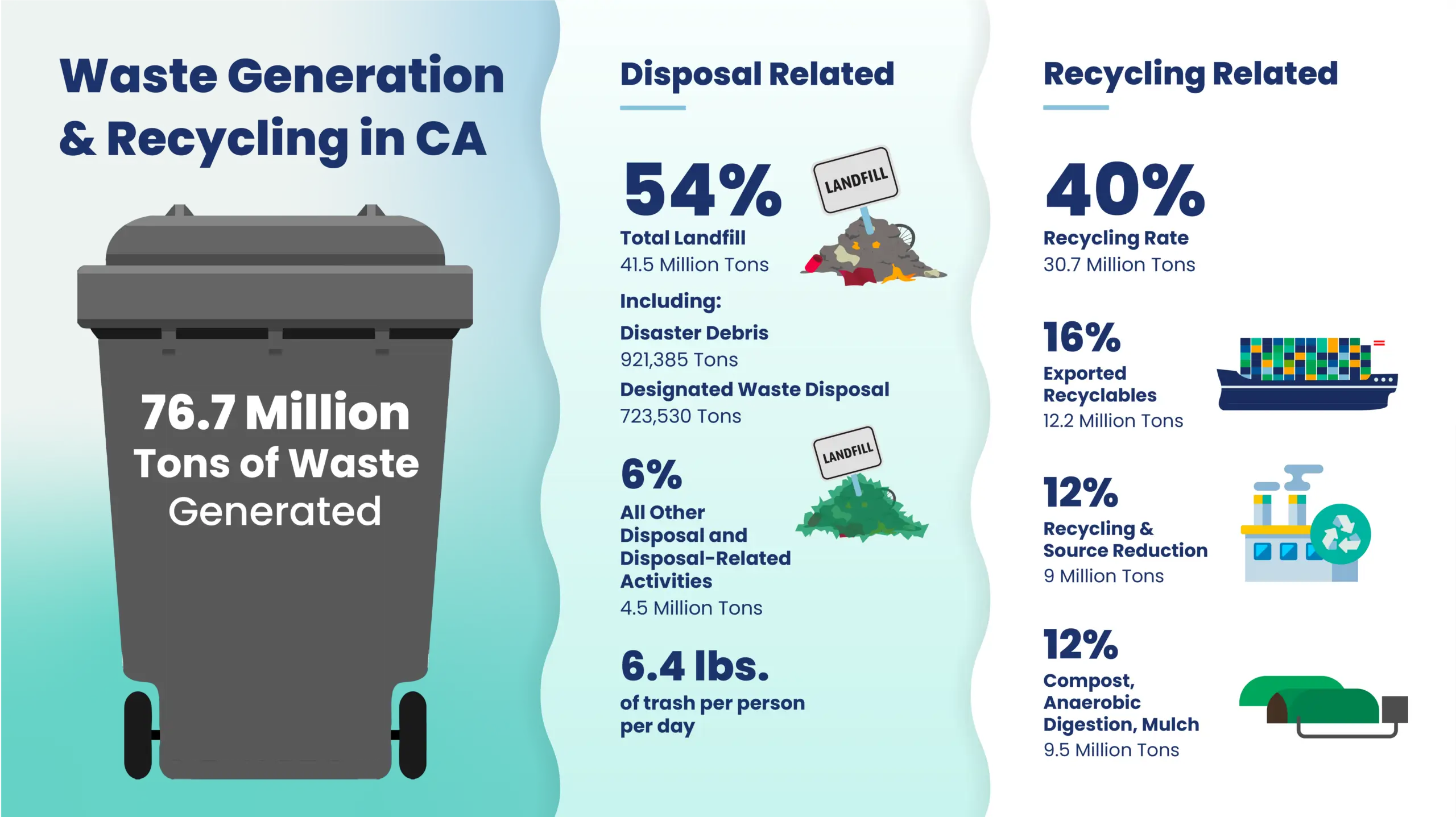
According to CalRecycle, the state agency responsible for managing waste disposal and recycling, California generated approximately 77.2 million tons of waste in 2020. This staggering figure not only encapsulates the scale of the challenge but also illustrates the potential benefits that effective recycling practices could unlock.
Despite progressive regulations aimed at promoting recycling, including the California Integrated Waste Management Act of 1989 that mandated each city to divert at least 50% of its waste from landfills, the state’s recycling rate has been a point of concern. The state’s statutory goal was to achieve a 75% recycling rate by the year 2020. However, as of the end of 2020, the recycling rate was significantly short of this target, hovering just below 50%.
One of the key reasons for the lower-than-expected recycling rate is the complexity and cost of waste sorting. Not all waste can be recycled, and separating recyclable waste from non-recyclable waste is a significant challenge. To recycle effectively, waste needs to be separated at the source, which often does not occur.
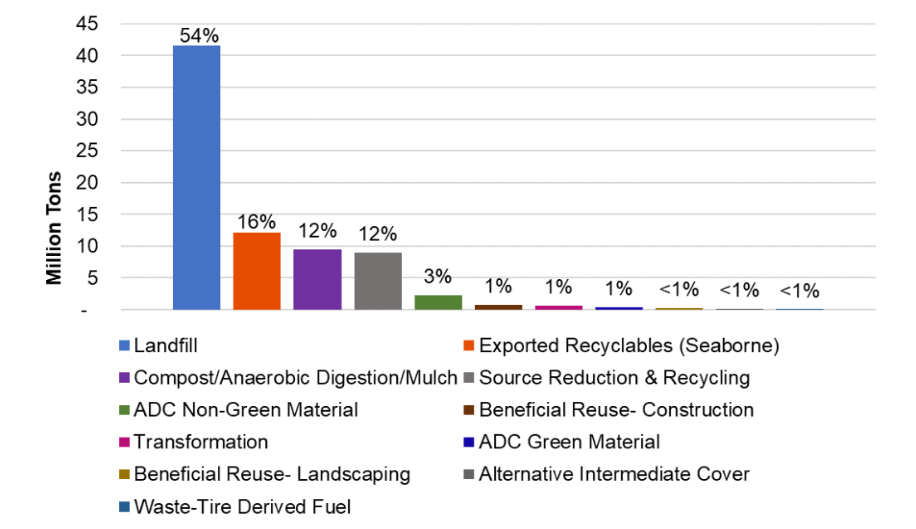
Additionally, the state’s dependence on overseas markets for recycling has also had an impact. A significant amount of California’s recyclable waste used to be shipped to China. However, the introduction of China’s National Sword Policy in 2018, which severely limited the import of recyclable materials, disrupted this practice. The policy led to a global reshuffling of recycling economies and impacted California’s ability to offload its recyclable waste, affecting the overall recycling rate.
It’s not all bad news, though. Despite the challenges, California continues to be at the forefront of recycling initiatives. The state’s Bottle Bill, officially known as the California Beverage Container Recycling and Litter Reduction Act, is one such initiative. The program incentivizes recycling by offering Californians refunds for returning used beverage containers. This program has been successful, boasting a recycling rate of over 75% for eligible beverage containers.
Another positive is the growing trend of organic waste recycling. In California, organic waste makes up more than a third of the material in the state’s waste stream. The state has made strides in this area with the implementation of regulations aimed at increasing organic waste recycling. California’s Mandatory Commercial Recycling law requires businesses to recycle their organic waste, helping to divert significant amounts of waste from landfills.
Overall, while California’s recycling rate may not have reached its ambitious goal, there is a clear framework in place for improvement. Understanding the current landscape of recycling in California – the successes, failures, and the challenges – is the first step in formulating effective strategies to boost the state’s recycling rate. The path forward involves building on the successful initiatives and addressing the identified challenges to create a more sustainable and effective recycling infrastructure in the state. As we move forward in this article, we’ll explore these strategies in greater detail.
2. The Importance of Improving California’s Recycling Rate
Recycling is more than a sustainability buzzword or a feel-good environmental initiative. It is a pivotal strategy in waste management that has profound environmental, economic, and social implications. For a state like California, with its vast population and significant economic activity, the importance of improving recycling rates cannot be overstated. An enhanced understanding of the “benefits of recycling,” the “economic impact of recycling,” and the correlation between “recycling and environment” underlines the gravity of this issue.
2.1 Environmental Benefits
The environmental benefits of recycling are multifaceted. A primary advantage is the reduction of waste sent to landfills and incinerators. With over 77 million tons of waste generated in California annually, effective recycling can significantly minimize landfill usage, alleviating the associated environmental concerns. These concerns range from methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming, to groundwater contamination and the destruction of natural habitats for landfill expansion.
Recycling also curbs the extraction of raw materials, preserving natural resources and ecosystems. The production of goods from recycled materials often requires less energy than creating the same goods from virgin materials. For example, producing aluminum from recycled cans uses 95% less energy than producing it from bauxite ore. Furthermore, less energy consumption means fewer fossil fuel burning and reduced carbon emissions, thereby mitigating the impacts of climate change.
2.2 Economic Advantages
The economic impact of recycling is significant. An efficient recycling system not only curbs the costs associated with waste disposal but also drives job creation. Recycling and remanufacturing industries in the U.S. generate over $200 billion in economic activity and sustain over a million jobs, as per the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Moreover, recycling contributes to a circular economy. A circular economy aims to keep resources in use for as long as possible, extract the maximum value from them while in use, then recover and regenerate products and materials at the end of each service life. This model can foster local industry growth, reduce dependency on raw material imports, and provide a buffer against market volatility for commodities.
2.3 Social Implications
Recycling has far-reaching social implications. At a fundamental level, it cultivates a culture of sustainability, making citizens active participants in environmental stewardship. By improving recycling rates, California can advance environmental literacy and influence behaviors, encouraging its residents to make more sustainable choices.
Furthermore, recycling can address social equity issues. By creating green jobs, it can contribute to poverty reduction and community development. Meanwhile, by reducing the need for landfills, which are often situated in underprivileged areas, it can alleviate associated health and quality of life issues in these communities.
3. Detailed Strategies to Improve California’s Recycling Rate
Addressing the shortfall in California’s recycling rates necessitates an integrated approach encompassing various strategies. From educating the public and strengthening waste management infrastructure to implementing legislative changes and promoting the circular economy, a multi-faceted plan can significantly enhance recycling rates.
3.1 Public Education and Awareness
Public education is a critical component of any successful recycling strategy. Often, the success of recycling initiatives hinges on widespread participation from community members who are informed and understand the value and process of recycling. Emphasizing “recycling education” and enhancing “public awareness recycling” can, therefore, significantly influence the effectiveness of recycling efforts.
Consider, for instance, the case of San Francisco, one of the cities with the highest recycling rates in the United States. A key factor contributing to this success has been robust public education campaigns aimed at reducing contamination and improving the quality of recyclables. The city uses a variety of communication channels, including websites, social media, print materials, and public service announcements to deliver clear, consistent messaging about recycling.
Community engagement initiatives, like workshops, school programs, and neighborhood clean-up drives, can also enhance awareness and motivate participation in recycling efforts. Implementing such initiatives on a broader scale across California could result in higher recycling rates.
Moreover, the development and dissemination of educational resources detailing what can and cannot be recycled, the importance of clean recyclables, and the impact of recycling on the environment and economy can help debunk recycling myths and overcome recycling apathy.

3.2 Strengthening Waste Management Infrastructure
The backbone of any successful recycling program is a robust waste management infrastructure. Upgrading California’s “waste management infrastructure” with efficient “waste sorting systems” and state-of-the-art “recycling facilities” can have a significant impact on recycling rates.
Improved waste sorting systems can help reduce contamination and increase the quantity and quality of recyclables. Systems like automated sorting lines and optical sorters can segregate waste more accurately and efficiently. On the other hand, advanced recycling facilities equipped with the latest technology can process a wider range of materials and handle larger volumes of recyclables.
Moreover, expanding recycling infrastructure to rural and underserved areas can help increase overall recycling rates. Developing recycling drop-off centers, expanding curbside pickup services, and increasing the accessibility of recycling facilities can make recycling more convenient for residents, thus promoting higher participation rates.
Investing in research and development can also lead to innovative solutions for recycling hard-to-recycle materials, expanding the range of recyclable materials and further boosting recycling rates.
3.3 Legislation and Policy Changes
Policy changes and new legislation play an instrumental role in enhancing recycling rates. Laws and policies can create an enabling environment that fosters recycling and makes it a standard practice rather than a voluntary act.
Possible policy interventions could include mandatory recycling laws, landfill bans for recyclable materials, and pay-as-you-throw programs that charge residents based on the amount of waste they generate. Extended producer responsibility laws, which hold manufacturers responsible for the post-consumer management of their products, can also incentivize waste reduction and recycling.
Legislation can also target specific sectors or materials. For instance, in response to the high volumes of food waste, California has enacted legislation requiring businesses to recycle their organic waste. Similar legislation targeting other high-volume waste streams could help boost overall recycling rates.
It’s crucial, however, that any “recycling legislation” or “waste management policies” introduced are accompanied by the necessary support, including education, infrastructure, and enforcement to ensure their effectiveness.
3.4 Promoting Circular Economy
Promoting a circular economy is another strategy that could significantly enhance recycling rates in California. A “circular economy” is one that emphasizes the reuse and recycling of materials to minimize waste and make the most of resources.
Encouraging “business recycling” and creating “recycling incentives” can help transition California towards a more circular economy, which could significantly improve recycling rates.
Businesses can play a crucial role in this transition by adopting sustainable practices, including reducing waste, incorporating recycled materials into their products, and designing products to be more easily recycled at the end of their lifecycle. Government incentives such as tax breaks or grants could be used to encourage businesses to adopt these practices.
For instance, the CalRecycle Recycling Market Development Zone loan program provides direct loans to businesses that use materials from the waste stream to manufacture their products and create jobs. This kind of program not only promotes recycling but also stimulates local economies.
Moreover, establishing or expanding public-private partnerships could lead to innovative recycling solutions. Companies could be incentivized to develop new technologies or processes for recycling materials that are currently difficult to recycle.
In the public sector, procurement policies favoring products made from recycled materials can drive demand for such products, promoting their production and, by extension, the recycling of materials.
Promotion of a circular economy should also consider the role of consumers. Public education campaigns can encourage consumers to choose products made from recycled materials or designed to be recyclable.

4. Case Studies of Successful Recycling Strategies
When aiming to improve recycling rates, examining “successful recycling programs” and learning from “recycling case studies” can provide invaluable insights. By understanding the “best recycling practices” implemented within California and beyond, policymakers can glean practical strategies to boost California’s recycling rates.
4.1 Recycling Strategies of San Francisco, California: Case Study
San Francisco, often hailed as the gold standard in recycling in the U.S., boasts an impressive 80% diversion rate as of 2020. One of the key strategies underpinning this success is the city’s three-stream waste collection system. Residents are provided with three separate bins: one for compost, one for recyclables, and one for landfill waste. Clear labels and public education campaigns help residents sort waste correctly, significantly reducing contamination.
The city also implements strong legislation, including a mandatory recycling and composting ordinance that requires all residents and businesses to sort waste. Additionally, San Francisco has banned certain hard-to-recycle materials, such as plastic bags and styrofoam, thus reducing waste and encouraging the use of more easily recyclable materials.
The city’s Zero Waste program, aiming to achieve zero waste to landfill by 2030, continuously evolves to address emerging challenges and opportunities. This approach of continuous improvement and adaptation, coupled with a robust legislative framework and widespread public participation, contributes to the city’s high recycling rate.

4.2 Recycling Strategies of Curitiba, Brazil: Case Study
Internationally, the city of Curitiba in Brazil has one of the most successful recycling programs, with an impressive recycling rate of approximately 70%. Curitiba’s success is largely due to its innovative Green Exchange Program. This program allows residents in underserved communities to exchange bags of recyclables for fresh produce. The program encourages recycling, reduces waste, and addresses food insecurity, thus creating a win-win situation for the city and its residents.
The city also runs a comprehensive environmental education program that reaches schools, businesses, and community groups. This program not only encourages participation in the city’s recycling initiatives but also fosters a culture of environmental stewardship.
4.3 Recycling Strategies, Oregon Bottle Bill: Case Study
On a state level, Oregon’s Bottle Bill presents a successful strategy to increase the recycling of specific materials. The law, introduced in 1971, created a container deposit system that provides a 10-cent refund for every beverage container returned to a redemption center. As a result, the state boasts a redemption rate of approximately 86% for eligible containers, well above the national average.
This policy demonstrates how financial incentives can drive recycling and reduce litter. The success of the Bottle Bill has led to its expansion over the years, covering a wider range of beverage containers and increasing the refund value.

4.4 Lessons Learned
These case studies underline the importance of comprehensive, multifaceted strategies in boosting recycling rates. Public education, strong legislation, innovative programs, and financial incentives all play a role in creating successful recycling initiatives.
The San Francisco case demonstrates the impact of a robust waste sorting system, stringent legislation, and public participation. Curitiba shows how recycling programs can also address other social issues, while the Oregon Bottle Bill highlights the power of financial incentives.
While these strategies need to be adapted to local contexts, they provide a blueprint for improving recycling rates in California and other regions. The case studies also emphasize that successful recycling programs require continuous monitoring and adaptation to changing circumstances and emerging opportunities.
Therefore, while improving California’s recycling rate poses significant challenges, these can be addressed through informed, innovative, and committed action. By learning from successful recycling strategies both within the state and globally, California can create a more sustainable, effective, and inclusive recycling system that benefits its environment, economy, and people.
FAQ’s
What is California’s current recycling rate?
As per 2023 data, the recycling rate in California was approximately 37%. However, the recycling rate can vary significantly from year to year based on numerous factors, including changes in waste generation, recycling program efficacy, and market conditions for recyclables. For the most current data.
Why is California’s recycling rate important?
California’s recycling rate is crucial as it reflects the state’s commitment to sustainability and waste reduction. Higher recycling rates mean fewer materials are sent to landfill, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving natural resources, and promoting economic development through the creation of jobs in the recycling industry.
What is being done to improve California’s recycling rate?
Several strategies are being employed to improve California’s recycling rate, including public education campaigns, strengthening waste management infrastructure, enacting legislation and policies to promote recycling, and encouraging a circular economy. These efforts involve various stakeholders, including the government, businesses, and individual citizens.
What are the challenges to recycling in California?
Challenges to recycling in California include contamination of recyclables, insufficient recycling infrastructure, particularly in rural areas, lack of public awareness about correct recycling practices, and market challenges such as low prices for recyclables and limited demand for certain types of recycled materials.
How can I help improve California’s recycling rate?
Individuals can help improve California’s recycling rate by practicing proper recycling habits, such as cleaning recyclables and sorting waste correctly. They can also reduce, reuse, and recycle waste, buy products made from recycled materials, participate in local recycling programs, and advocate for policies promoting recycling.
How does California’s recycling rate compare to other states?
As of 2023, California’s recycling rate was approximately 37%, which is lower than some states but higher than others. Comparing recycling rates across states can be challenging due to differences in how recycling rates are calculated and what materials are included in the calculations.
What is the goal for California’s recycling rate?
California has set an ambitious goal of 75% recycling, composting, or source reduction of solid waste by 2030 through the implementation of AB 341. Achieving this goal requires concerted effort from all sectors of society, including state and local governments, businesses, and individuals.
What materials are most commonly recycled in California?
Commonly recycled materials in California include paper, cardboard, glass, metal cans, and certain types of plastic. However, the list of recyclable materials can vary by location due to differences in local recycling programs and facilities.
Does California have mandatory recycling laws?
Yes, California has several mandatory recycling laws. For example, the Mandatory Commercial Recycling Law (AB 341) requires businesses that generate a certain amount of waste and multi-family dwellings with five or more units to recycle.
What is the impact of California’s recycling rate on the environment?
A higher recycling rate in California would result in less waste going to landfills, which could decrease greenhouse gas emissions, reduce pollution, conserve natural resources, and promote biodiversity. Additionally, recycling can save energy compared to extracting and processing virgin materials.
Read More